OT cyber hygiene encapsulates a range of best practices designed to prevent, detect, and mitigate cyber threats within industrial networks.
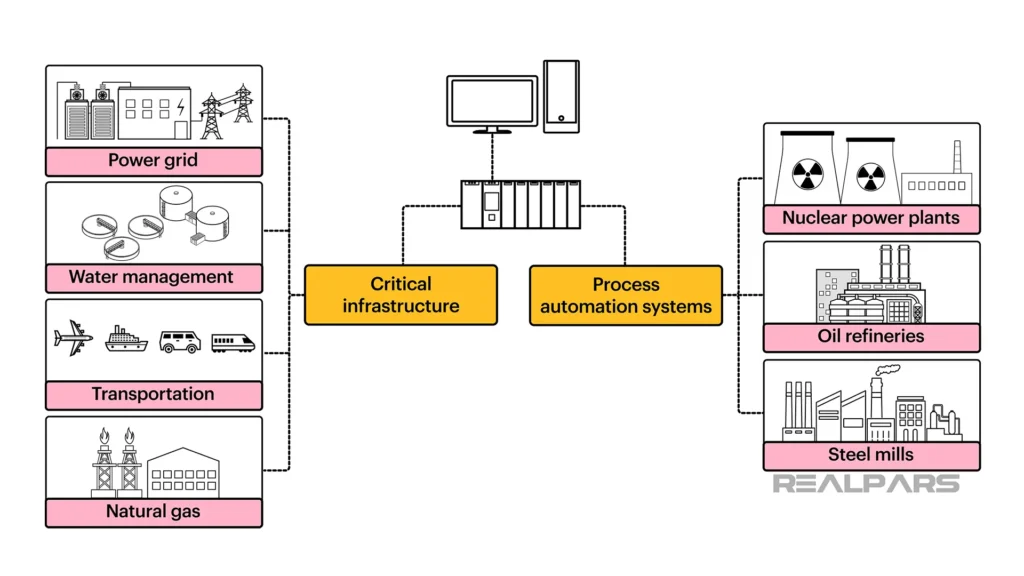
In the digital age, where industrial operations rely increasingly on interconnected systems and automation, the importance of cybersecurity cannot be overstated. Operational Technology (OT) networks, which control critical infrastructure and industrial processes, are prime targets for cyber attacks. To safeguard against these threats, organizations must prioritize OT cyber hygiene – a set of essential practices aimed at maintaining the health and security of industrial networks. Join us as we explore the key principles of OT cyber hygiene and how they can help protect against cyber threats in industrial environments.
Understanding OT Cyber Hygiene:
OT cyber hygiene encompasses a range of best practices designed to prevent, detect, and mitigate cyber threats in industrial networks. At its core, it involves maintaining a strong security posture through regular maintenance, updates, and adherence to security protocols. Just as personal hygiene is essential for staying healthy, OT cyber hygiene is crucial for ensuring the integrity and reliability of industrial operations.
Essential Practices:
- Patch Management: Regularly update and patch OT systems and software to address known vulnerabilities. Many cyber attacks exploit outdated software and unpatched systems, making patch management a critical aspect of OT cyber hygiene.
- Network Segmentation: Implement network segmentation to isolate critical OT assets from less secure networks, such as enterprise IT environments or the internet. This limits the impact of potential cyber attacks and reduces the attack surface of industrial networks.
- Access Control: Restrict access to OT systems and devices based on the principle of least privilege. Only authorized personnel should have access to critical assets, and access should be monitored and logged to detect unauthorized activity.
- Security Awareness Training: Educate employees about the importance of cybersecurity and their role in maintaining OT cyber hygiene. Training programs should cover topics such as phishing awareness, password security, and incident response procedures.
- Asset Inventory and Management: Maintain an accurate inventory of OT devices, systems, and software deployed in industrial environments. Regularly review and update the inventory to ensure visibility and control over all assets.
- Continuous Monitoring: Implement robust monitoring solutions to detect and respond to anomalous activity in real-time. This includes network traffic analysis, intrusion detection systems, and security event logging.
- Incident Response Planning: Develop and regularly test incident response plans to ensure a timely and effective response to cyber incidents. Organizations should have clear procedures in place for containing, investigating, and mitigating cyber attacks in industrial environments.
Benefits of OT Cyber Hygiene:
Adopting a proactive approach to OT cyber hygiene offers several benefits for organizations operating in industrial sectors:
- Reduced Risk of Cyber Attacks: By implementing essential practices such as patch management and access control, organizations can reduce the likelihood of successful cyber attacks on industrial networks.
- Increased Operational Resilience: A strong security posture enhances the resilience of industrial operations against cyber threats, minimizing disruption and downtime.
- Regulatory Compliance: Many industries are subject to regulatory requirements related to cybersecurity. By following OT cyber hygiene best practices, organizations can demonstrate compliance with industry regulations and standards.
- Protection of Critical Assets: OT cyber hygiene helps protect critical assets and infrastructure from cyber threats, safeguarding the integrity and reliability of industrial operations.
Lear about iOT365 Risk Assessment Tool
Conclusion:
In today’s interconnected world, OT cyber hygiene is essential for protecting industrial networks against cyber threats. By implementing essential practices such as patch management, network segmentation, and access control, organizations can enhance the security and resilience of their OT environments. Remember, good cyber hygiene is not a one-time effort but an ongoing commitment to maintaining the health and security of industrial networks. With a proactive approach to cybersecurity, organizations can mitigate the risks posed by cyber threats and ensure the continuity of critical operations.