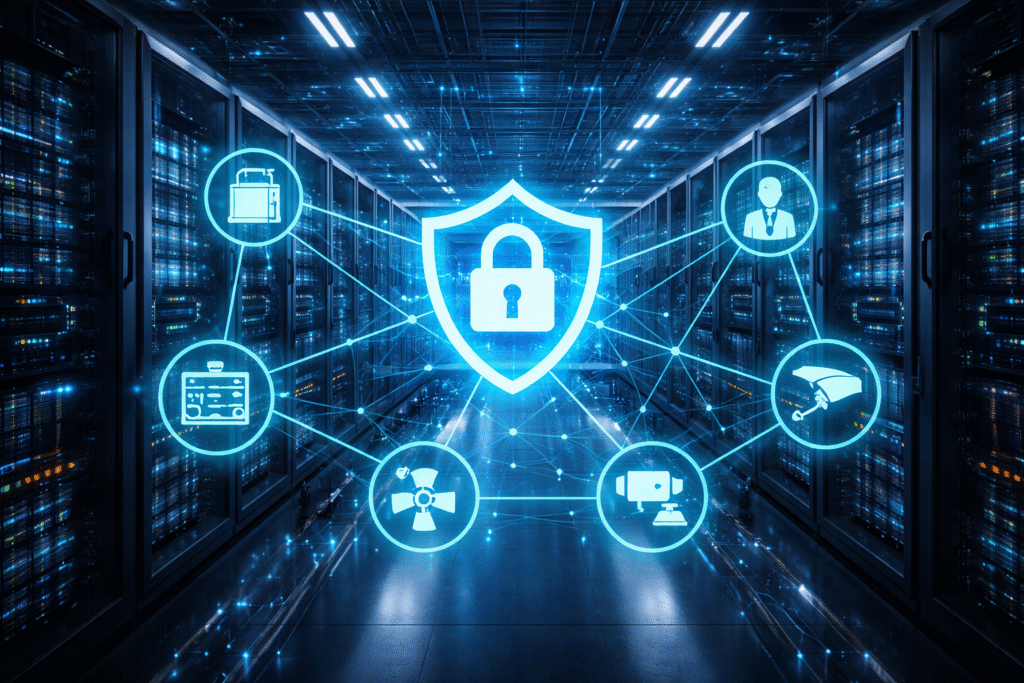
Data Center Cybersecurity: Critical OT and IoT Risks
Data centers rely on OT and IoT systems to operate every day. These systems manage power, cooling, and security. However, many were not built with cybersecurity in mind. As a result, attackers are targeting these facilities more often.
Why Data Centers Are High-Value Targets
To begin with, data centers support cloud services and critical workloads. Any disruption can cause major downtime. However, many supporting systems were not designed with security in mind.
Additionally, data centers use a mix of legacy OT and modern IoT devices. Therefore, visibility gaps are common.
For example, attackers may target power management systems. Moreover, cooling failures can shut down entire facilities. Finally, outages can impact many customers at once.
Threat #1: Power and Electrical Systems
First, data centers depend on OT systems for power distribution. These include UPS systems, generators, and switchgear. However, many controllers use outdated protocols.
Additionally, remote monitoring is common. For example, vendors often access power systems remotely.
As a result, attackers may exploit weak access controls.
Threat #2: Cooling and Environmental Controls
Secondly, cooling systems keep servers within safe temperatures. These systems rely on sensors, PLCs, and automation controllers. However, many lack encryption or strong authentication.
In addition, cooling systems often share networks with IT assets. Therefore, attacks can spread quickly.
Consequently, even a small disruption can cause major outages.
Threat #3: IoT Sensors and Monitoring Devices
Thirdly, data centers use many IoT devices. These include temperature sensors, cameras, and access controls. However, many devices ship with default settings.
For example, some sensors use weak passwords. Additionally, firmware updates may be rare.
As a result, IoT devices become easy entry points.
Threat #4: Vendor and Third-Party Access
Fourthly, vendors often manage OT and IoT systems remotely. This access supports maintenance and monitoring. However, access controls are not always enforced.
Moreover, shared credentials are still common. Therefore, tracking activity becomes difficult.
Consequently, stolen credentials can expose critical systems.
How IoT365 Helps Secure Data Centers
In response to these risks, IoT365 provides full visibility across OT and IoT assets. The platform monitors devices without disrupting operations.
Additionally, IoT365 applies Zero Trust segmentation. Furthermore, it detects abnormal behavior in real time.
As a result, operators reduce risk and improve uptime.
- Real-time device discovery across OT and IoT
- Zero Trust segmentation to limit lateral movement
- Password and firmware checks
- Anomaly detection for unsafe activity
- Secure vendor access with identity tracking
Related OT & IoT Cybersecurity Resources
To explore similar risks across industries, review these IoT365 resources:
- Manufacturing OT & IoT Cybersecurity Risks
- Water Utility OT & IoT Cybersecurity
- Healthcare OT & IoT Cybersecurity
Learn More from Trusted Data Center Security Sources
- CISA – Critical Infrastructure Security
- NIST Cybersecurity Framework
- Uptime Institute – Data Center Resilience
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, data centers must secure OT and IoT systems. However, many facilities still rely on outdated controls.
Ultimately, strong cybersecurity protects uptime and customer trust.